Data you are trying to protect behind encrypted passwords and firewalls can still manage to slip right through your fingers. That is why it’s so imperative to understand how data loss and leakage can occur and what steps must be taken in order to prevent it. In this article, we’ll define data loss and data loss prevention procedures. Additionally, we will provide a list of data loss prevention solutions, which can help you protect your business against potential data losses and breaches.
The statistics behind recent malware and phishing attacks in light of the pandemic are rather striking. According to ForgeRock’s Consumer identity report, in the first quarter of 2020, more than 1.6 billion consumer records were impacted by breaches. Businesses shifting their operations to home offices to ensure business continuity are at a greater risk for data loss and leakage.
Besides the pandemic, there are other factors that are driving the adoption of data loss prevention policies, such as the evolving compliance requirements (GDPR or NYDFS) and availability of different solutions and places to protect your data (cloud storage, supply chain networks).
Data Loss Prevention Definition
Before we dive into data loss prevention, it’s important to explain what data loss is and define any other terms associated with it.
According to Wikipedia, “data loss is an error condition in information systems in which information is destroyed by failures or neglect in storage, transmission, or processing.”
Data unavailability, which can happen due to a network outage, should not be mistaken for data loss. Even though the two have similar consequences for users, data unavailability is not permanent.
Several other concepts exist that are often used interchangeably with data loss, such as: data breach, which occurs when the data falls into the wrong hands, and data leak, in which media with sensitive information gets lost (although sometimes not lost on the originating side) and is subsequently acquired by an unauthorized party.
To prevent data loss or restore lost data, companies implement backup and disaster recovery processes.
Data loss prevention (or DLP) is a set of tools, processes, and practices to ensure that data is protected from loss, misuse, or access by unauthorized parties.
Data loss prevention software detects potential data breaches and prevents them by blocking sensitive data while in use, in motion, or at rest. DLP software also provides reporting to meet the requirements of compliance, auditing, and forensics. While there is no one-fits-all solution, there is a long list of data loss prevention products available. Keep on reading to learn how they differ.
Other terms that are associated with data loss and leakage prevention include:
- Information leak detection and prevention (ILDP)
- Information leak prevention (ILP)
- Content monitoring and filtering (CMF)
- Information Protection and Control (IPC)
- Extrusion Prevention System (EPS)
The DLP tools and procedures can be divided into the following categories:
- Standard security measures, which include firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDSs), and antivirus software.
- Advanced security measures, which employ machine learning and temporal reasoning algorithms, honeypots and activity-based verification, and user activity monitoring.
- Access control and encryption.
- Designated DLP systems that use exact data matching, structured data fingerprinting, statistical methods, rule and regular expression matching, conceptual definitions, published lexicons, and other data (loss) identification mechanisms.
Data Loss Prevention Components
Data loss prevention can be broken down into the following components:
- Preventing data loss in motion
Data in motion or network traffic is protected by the network technology, which is typically installed at network egress points near the perimeter. The central management server analyzes network traffic from multiple security control points and looks for sensitive data that is sent in violation of information security policies.
- Securing endpoints and protecting data in use
Data while in use or endpoint systems run on internal end-user workstations or servers. End-point based technology (just like a network technology) addresses both internal as well as external communications and is used to control information flow between different groups and types of users. End-point based agents can also block attempted communication, provide user feedback, monitor and control access to physical devices, and even access information before it’s encrypted. DLP systems monitor and flag unauthorized activities (whether intentional or not), such as screen capture, copy and paste, printing, and faxing of potentially sensitive information.
- Protecting data at rest
Data at rest or data storage can be protected by access control and encryption with the appropriate data retention policies in place.
- Identifying data to be protected
Data identification technology, sometimes confused with data discovery, determines what data to look for and includes techniques aimed at identifying confidential and sensitive information.
- Detecting data leaks
Detecting data leaks is identifying data transfers that are suspicious or anomalous and alerting staff about potential leakage.
Data Loss Prevention Examples
Let’s look at some of the data loss prevention use cases that can help identify and stop potential threats in your organization. This will provide a better understanding of the scope of the problem and its importance.
REA Group is a multinational digital advertising agency that addressed DLP while restructuring its IT policy amid global expansion. Since REA is a cloud-first company with 90% of systems being SaaS-based, it needed to achieve the desired ability to monitor cloud usage. For that specific purpose, REA partnered with McAfee and opted for McAfee’s MVISION Cloud solution, which helped them achieve the appropriate security levels and prevent data loss while expanding and scaling upward.
Accenture, a global leader in technology solutions and services, built their own DLP ecosystem. The company deployed DLP agents on every workstation to monitor the data flow and report back to the security center. Accenture also developed its own set of rules to red-flag, prevent, or block file transfer of client data when sent to unauthorized devices, as well as implemented email DLP to prevent potential leakage of sensitive data through emails.
Stahl, a pharmaceutical company based in the Netherlands, identified its biggest threat/concern as the potential data leakage or loss through mobile devices. Since most employees worked from home, it was critical to monitor activities on those devices. For that specific reason, they partnered with DeviceLock, who helped the company develop a system to monitor, assess, and block the transmission of sensitive data to unauthorized parties.
Data Loss Prevention Best Practices
Implementing data loss prevention policies is not easy but can be accomplished by following the best practices for DPL deployment.
- First, you need to prioritize data because not all of it is equally important. DPL should start from the data whose loss would cause significant disruption to your business.
- Determine your primary objective of enforcing DPL policies: to protect your intellectual property, meet compliance standards, or gain more visibility of your data. By determining your goals, you’ll understand which DLP architecture best suits your needs. Among the four main types are Endpoint DLP, Network DLP, Discovery, or Cloud.
- All data must be classified and associated with the source application, the user, or the datastore. Continuous classifying and tagging of data will make it easily trackable.
- DPL policies must account for the mobility of data and when it’s at risk. For example, the risk of losing data is higher when it’s in use on endpoints, such as when it’s shared with partners, customers, and end-users.
- Talking with line managers and identifying problem areas are both crucial for creating controls which reduce at risk data. As the DLP policies mature, so do the controls, which become more fine-tuned and granular.
- Training employees and educating them about data loss can prevent accidental data breaches and leaks. Continuous training and engagement of employees essentially blocks risky activities and streamlines the DLP adoption.
The specifics of DLP deployment largely depend on your IT infrastructure. Below are a few simple Data Loss Prevention techniques that can protect your business and personal information from data loss:
- Build your DLP strategy on a backup solution: make backup copies of essential information on a regular basis.
- Spread your backups and assets across different devices and solutions. Never store all your backups in one place. Ideally, combine both cloud and physical solutions.
- Use sophisticated anti-virus software and install updates as soon as they become available.
- Ensure your system is protected by a robust firewall to keep unsafe traffic outside of your network.
- Limit access to data with encrypted passwords and change them every three months.
- Encrypt all other information.
Data Loss Prevention Software & Tools
Data Loss Prevention software runs differently from other security software like disaster recovery, endpoint security, or employee monitoring software. DPL software goes even further than the above-mentioned tools by employing a proactive rather than a reactive approach to safeguarding data.
Data Loss Prevention tools often use AI to monitor suspicious activities. This ensures that anything outside normal behavior is stopped before the data gets damaged or lost.
Moreover, it usually answers or is tailored to specific compliance regulations, such as GDPR.
Since good DPL software is paramount for businesses, it’s important to understand what options exist. Herein, we’ll provide a list of reliable DPL tools from which you can choose the solution that’s right for you.
Paragon PCB SDK
As part of the DLP strategy, your business needs to have a solid backup solution. Paragon Open Cloud Backup Platform offers a full set of tools to develop your own robust backup solution of any size. You can also leverage the completed backup solution that’s already in store.
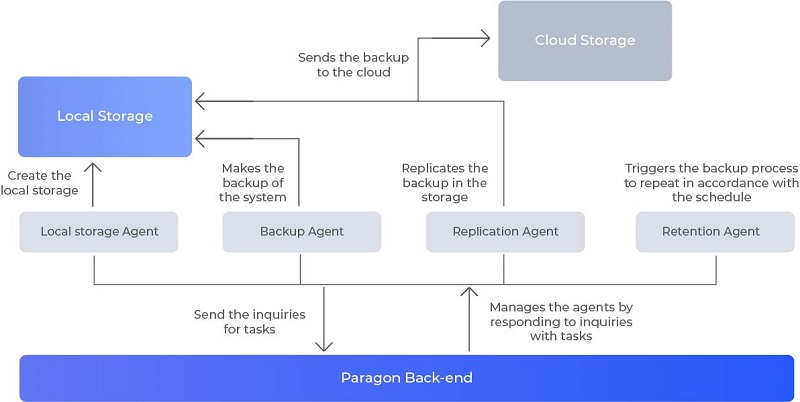
Paragon PCB SDK consists of the following components:
- Backup model framework
- Load forecasts reports
- Local agents bundle (that comprises backup agent, replication agent, and local worker)
- Cloud storage access
- Documents and instructions
A Cloud Backup SDK leverages microservices (such as inventory, registry, storage, notification services, and so forth) to manage all SDK components.
All set components work conjointly to fulfill backup tasks as shown in the scheme below:
Depending on what objects you need to backup, it will be either agentless backup for virtualized environments (Hyper-V, VMware vSphere) or will require a set of agents to be installed on the endpoints for physical backup.
Azure
Azure Information Protection (AIP) is a cloud-based solution that helps businesses classify and protect their documents and emails by applying labels either automatically or manually.
Automatic labeling can be enabled by administrators with the help of rules and conditioning. Manual labeling can be set up by users. Both automatic and manual labeling means that administrators define the recommendations shown to users.
Labels can classify and protect information by allowing users and administrators to:
- Track and control how data is used
- Analyze data flows
- Detect risky behaviors and take corrective measures
- Track access to documents and files
Labeling includes:
- Classification (regardless of where the data’s stored and with whom it’s shared)
- Marking (headers, footers, watermarks)
- Metadata (which can be added to files and email headers in the text that can be recognized and acted on by other apps).
AIP uses the Azure Rights Management service (Azure RMS), which is integrated with other Microsoft services like Office 365 and Azure Active Directory and can be used with third-party apps or information protection software.
Azure RMS uses encryption, identity, and authorization policies. Protection policies can be either used on their own (by apps and services that support protection but not labeling) or be a part of a label configuration (where users can simply apply a label to classify and protect documents).
By activating Azure RMS, administrators can either use the predefined templates or configure unique protection settings and apply more restrictive controls.
The AIP client installs the Information Protection bar to all Office apps and instantly enables users to integrate AIP within their docs and emails (by selecting appropriate labels and classifications).
Additionally, for the Information Protection bar there’s a Classify and protect menu option, which works similarly and enables users to customize the permissions.
AIP also enables admins to classify and protect documents that have already been created and stored on-premises, in the cloud with Azure Information Protection scanner (for on-premises), and Microsoft Cloud App Security (for docs stored on cloud).
G Suite & Google Drive
G suit allows admins to work with predefined templates or configure their own by assigning rules to the whole company’s domain, an organizational unit, or a group. In case sensitive content is detected, admins can set up actions to take.
DPL for Drive prevents users from sharing sensitive content in Google Drive or shared drive with people outside the company. DPL rules can be employed to scan files for sensitive content and warn users in case they try to share a file or block anyone outside the company from accessing that file. DPL for Drive scans sheets, docs, and slides (however, comments and forms are not supported).
New DPL for Drive allows admins to use advanced features that are not in the legacy DPL, such as match count in all conditions that use regular expressions, word lists, and predefined detectors or have more granular detection thresholds.
AWS
AWS offers an app called Amazon Macie, a fully managed data security and data privacy service. Macie employs machine learning and pattern matching that automates the discovery and protection of sensitive data at scale in AWS. Amazon’s DLP software provides an inventory of Amazon S3 buckets, as well as identifies and alerts admins of any sensitive data in the selected list of buckets. Macie’s findings are easily accessible in the AWS Management Console and can be used in combination with other AWS services or third-party apps to take automated actions.
Macie can be easily set up from the Console or through an API call. The app provides multi-account support using AWS Organizations, so it can be applied across all company’s accounts.
Macie offers a fully managed set of sensitive data types so that no configuration is required. However, admins can define their own custom sensitive data types, which will protect data that is unique to their business.
Symantec
Symantec Data Loss Prevention 15.7 is a sophisticated technology that enables organizations to:
- Discover sensitive data in cloud storage repos, on file and web servers, in databases, and on endpoints.
- Protect sensitive data through quarantine.
- Monitor the use of sensitive data on endpoints.
- Prevent transmission of sensitive data to unauthorized parties.
- Enforce data security and encryption policies.
Symantec DLP solution comprises the following components:
- Enforcer Server
- Network and Cloud Storage Discover
- Network Protect, Monitor, and Prevent
- Endpoint Discover and Prevent
The Discover, Protect, Monitor, and Prevent modules can be used in conjunction or deployed independently.
At the core of the DLP solution lies content-aware detection technology that makes it possible to detect sensitive data anywhere and in any format. Symantec applies advanced machine learning, image recognition, fingerprinting and describing technologies that classify data with limited false positives.
The distributed architecture of Symantec DLP solutions allows for central management of data security policies, reporting, and immediate deployment across the entire Symantec DLP suite, as well as scaling of data loss prevention policies in accordance with the size of the organization.
Symantec DLP integrates with other Symantec apps, such as Symantec Information Centric Security and the Integrated Cyber Defense Platform. It also supports integration with third-party apps.
McAfee
McAfee DLP suite identifies sensitive data or user activity, takes action, and creates incidents of violations.
McAfee Data Loss Prevention suite includes the following components:
- McAfee DLP Discover
- McAfee DLP Prevent
- McAfee DLP Monitor
- McAfee DLP Endpoint
The complex DLP solution allows businesses to protect data wherever it resides (on the network, in the cloud, and at the endpoints), remain compliant with automated reporting, and manage policies and incident workflows with flexible deployment options.
The main product features include:
- Capture technology that allows tracking how data is used and leaked.
- Data classification that identifies and classifies sensitive data.
- Encryption, quarantine, redirection, and blocking of sensitive data transmissions.
For example, for data in use, McAfee Endpoint and Device Control components track various user actions such as copying of data and files to removable media, printing of data, and taking screen captures. For data in motion, McAfee DLP Prevent (or McAfee DLP Prevent for Mobile Email) and McAfee DLP Monitor components keep track, analyze, and categorize local traffic on the company’s network, then store it in the McAfee DLP database. For data at rest, McAfee DLP Discover and McAfee DLP Endpoint discovery scan, track, and perform remedial actions on data residing in file shares, databases, and repositories.
Fortinet
FortiGate is a DLP solution from Fortinet that watches over sensitive data and prevents it from leaving your network. Data matching predefined patterns will be blocked or logged and allowed when passing through FortiGate. Admins can create individual filters based on file type or size, a regular expression, an advanced rule, or a compound rule. Besides preventing sensitive data from leaving your network, the solution also prevents unwanted data from entering your network and archives some or all content that passes through the FortiGate.
The FortiGate unit has a DLP sensor, which is essentially a package of filters that controls which traffic is allowed to pass or should be blocked. Each DLP sensor can have one or more predefined filters that examine files using DLP fingerprints, checks files of a specific type, name, or size, matches data against a regular expression, or analyzes traffic using an advanced or compound rule.
FortiGate also has a utility that can apply a digital watermark to files, which is a digital pattern that marks files as being proprietary and allows for definitive sensitivity levels.
Sophos
The data loss prevention functionality is included in the Sophos Endpoint and Email Appliance products. The Sophos solution offers a comprehensive set of sensitive data type definitions, which were created and are maintained by SophosLabs. These data type definitions can also be customized per your specific industry or business.
The DLP rule definitions can all be set up from a flexible point-and-click policy wizard, where admins can define the scope (endpoint, groups, email sender, recipient, or content) of the rules, criteria (file types, content), triggers (copying, burning, uploading), and actions (logging the events, warning users, quarantining, or blocking).
Sophos also offers a comprehensive DLP SDK, a cross-platform data security solution, for companies who want to implement DLP capabilities within their products. Sophos DLP SDK is built on anti-malware and content analysis engines that identify files, extract and convert text, and search for sensitive data. On top of that, it has a comprehensive library of sensitive data definitions that cover all common types of Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial, and healthcare data.
Forcepoint
Forcepoint Data Loss Prevention solution is posited as addressing the human-centric risk associated with data leakage and loss of sensitive data. It accomplishes this by exposing weak points and controlling all environments where people work and where data resides.
Admins can apply user-risk scoring to focus on events that matter most to an organization while accelerating compliance with global data regulations.
Forcepoint DLP comes with pre-packaged coverage of global regulations with over 350 applicable policies that meet the state demands of more than 80 countries.
Forcepoint DLP for Compliance offers the following features:
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
- Robust identification for Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
- Custom encryption identification
- Cumulative analysis for drip DLP detection
- Integration with Microsoft Azure Information Protection
Forcepoint DLP for IP Protection applies machine learning capabilities that can be leveraged to train the system to identify relevant data, uses fingerprinting of structured and unstructured data, and employs analytics to help identify changes in user behavior.
Forcepoint DLP allows for location and remediation of regulated data with network, cloud, and endpoint discovery. It can operate alone or be paired with Forcepoint Web Security or Forcepoint Email Security to provide a well-rounded security solution.
Forcepoint DLP Network includes Forcepoint DLP Email Gateway, which is deployed in Microsoft Azure, and supports the scanning of content supplied by third-party solutions.
Forcepoint Data Discovery can locate the sensitive data in on-premises data centers and cloud applications: it scans data on file and email servers, databases, and content collaboration applications.
Forcepoint DLP Endpoint prevents data loss over endpoint channels (mobile devices, removable storage devices, email clients, and etc.), can discover and remediate sensitive data on laptops or desktop systems, analyze content, and block or monitor Data Loss Prevention policy breaches.
The Forcepoint mobile agent applies the policies to corporate email traffic that synchronizes to mobile devices.
Watchguard
Watchguard DLP is a comprehensive solution that helps keep sensitive data private, prevents data breaches, and enforces compliance.
Watchguard DLP solution has the following main features:
- Library of over 200 rules for 18 countries (including compliance mandates like PCI DSS and HIPAA).
- Automatic updates of available rule sets.
- Seamless integration with WatchGuard Dimension, a tool that allows for inspection of total connections and the number of identified violations (including allowed, denied, and quarantined).
- Protection of sensitive data transmitted via email, web, and FTP.
- Parsing of data from more than 30 files types.
- Decompression of archived files for data extraction.
- Automatic updates of available rule sets.
Watchguard DLP solution examines outbound traffic using pattern matching. If sensitive information is identified, it triggers an action such as notifying an admin, quarantining or blocking the data. Although there are built-in data sensors, admins can also customize them and enforce other content control rules.






Leave a Comment